Blockchain Technology: Revolutionizing the Digital Landscape
Introduction
Blockchain technology has emerged as a groundbreaking innovation with the potential to revolutionize various industries. This decentralized and transparent system has gained immense popularity due to its secure and efficient nature. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of blockchain technology, its applications across different sectors, and its impact on the future of the digital landscape.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Blockchain Technology
- Key Components of Blockchain
- How Blockchain Works
- Applications of Blockchain Technology
- Finance and Banking
- Supply Chain Management
- Healthcare
- Real Estate
- Voting Systems
- Intellectual Property
- Digital Identity Management
- Energy Sector
- Charitable Organizations
- Data Security
- Advantages of Blockchain Technology
- Enhanced Security
- Transparency and Accountability
- Improved Efficiency
- Reduced Costs
- Elimination of Intermediaries
- Challenges and Limitations
- Scalability
- Regulatory Concerns
- Energy Consumption
- Integration Issues
- Privacy Concerns
- Future Trends in Blockchain Technology
- Conclusion
- FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. Understanding Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is a distributed ledger system that allows multiple parties to maintain a shared and immutable record of transactions. It operates on a peer-to-peer network, eliminating the need for intermediaries. The core concept of blockchain involves the creation of a chain of blocks, where each block contains a set of transactions. These blocks are securely linked using cryptographic hashes, ensuring the integrity of the data.
2. Key Components of Blockchain
The fundamental components of blockchain technology include:
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional systems, blockchain operates on a decentralized network, where no single entity has control over the entire system.
- Consensus Mechanism: Blockchain networks utilize consensus algorithms to validate and agree upon the state of the ledger.
- Cryptographic Security: Blockchain employs cryptographic techniques to secure data and ensure the authenticity and integrity of transactions.
- Smart Contracts: These self-executing contracts automate the execution of predefined terms and conditions without intermediaries.
3. How Blockchain Works
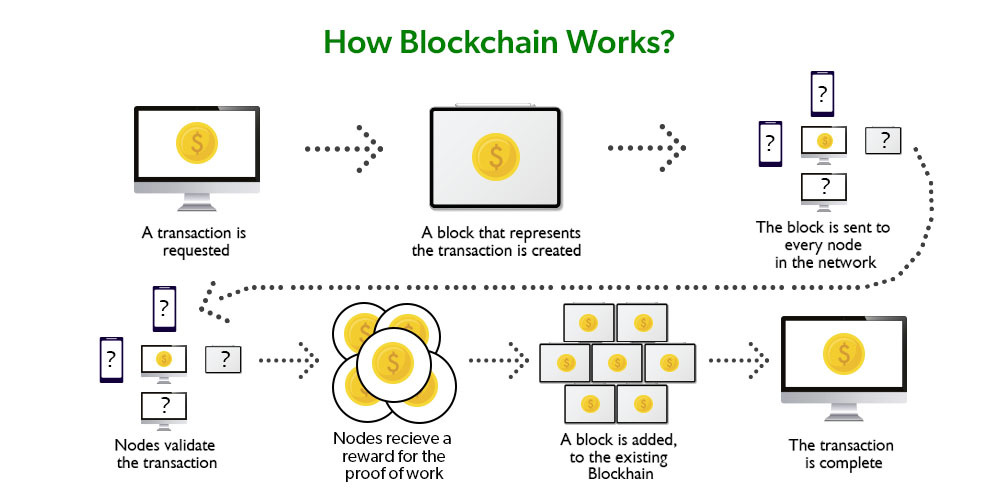
Blockchain technology operates through a series of steps:
- Transaction Initiation: Users initiate transactions by creating digital records containing relevant information.
- Verification: Miners or validators verify the transactions and group them into blocks.
- Block Formation: Verified transactions are added to a new block along with a unique identifier called a hash.
- Consensus: Miners reach a consensus on the validity of the block through consensus algorithms.
- Block Addition: Once consensus is achieved, the new block is added to the existing chain, forming an immutable record.
- Continuous Updating: The process repeats, and new transactions are added to the blockchain in a sequential manner.
4. Applications of Blockchain Technology
4.1 Finance and Banking
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the finance and banking industry by streamlining processes, reducing costs, and enhancing security. It enables faster cross-border transactions, eliminates intermediaries, and provides secure digital identities for users.
4.2 Supply Chain Management
Blockchain ensures transparency and traceability in supply chain management by recording every step of the process. It enables stakeholders to track the movement of goods, verify their authenticity, and detect fraudulent activities, thereby improving efficiency and trust.
4.3 Healthcare
Blockchain technology can enhance data interoperability and security in the healthcare sector. It enables secure sharing of patient records, reduces medical fraud, and facilitates drug traceability, ultimately leading to better patient care and improved research outcomes.
4.4 Real Estate
By leveraging blockchain technology, real estate transactions can become more transparent, efficient, and secure. Smart contracts can automate property transfers, streamline escrow processes, and eliminate the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and mitigating fraud.
4.5 Voting Systems
Blockchain-based voting systems can ensure the integrity and transparency of elections. By providing an immutable record of votes, it eliminates the possibility of tampering or manipulation, fostering trust in the democratic process.
4.6 Intellectual Property
Blockchain can revolutionize intellectual property management by providing a decentralized and tamper-proof registry. It enables artists, writers, and inventors to protect their creations, establish ownership, and ensure fair compensation for their work.
4.7 Digital Identity Management
Blockchain-based digital identity systems empower individuals to have control over their personal data. It offers a secure and verifiable way to authenticate identities, reducing identity theft and simplifying identity verification processes.
4.8 Energy Sector
Blockchain technology can facilitate peer-to-peer energy trading, where users can buy and sell excess energy directly without intermediaries. It promotes renewable energy adoption, ensures transparency in energy transactions, and facilitates efficient energy management.
4.9 Charitable Organizations
By utilizing blockchain technology, charitable organizations can enhance transparency and accountability in donation tracking. Donors can have a clear view of how their funds are utilized, fostering trust and encouraging more contributions.
4.10 Data Security
Blockchain provides robust data security by encrypting information and distributing it across multiple nodes. This decentralized storage system makes it difficult for hackers to breach the network and ensures the integrity of sensitive data.
5. Advantages of Blockchain Technology
5.1 Enhanced Security
Blockchain technology incorporates advanced cryptographic techniques, making it highly secure. The decentralized nature of the system, coupled with encryption, ensures that data remains tamper-proof and resistant to unauthorized modifications.
5.2 Transparency and Accountability
Blockchain offers unparalleled transparency as every transaction is recorded and accessible to all participants. This fosters trust among stakeholders and reduces the potential for fraudulent activities.
5.3 Improved Efficiency
By eliminating intermediaries and automating processes through smart contracts, blockchain technology streamlines operations and reduces inefficiencies. It enables faster transaction settlements, minimizes paperwork, and enhances overall productivity.
5.4 Reduced Costs
The removal of intermediaries and the automation of processes result in cost savings across various industries. Blockchain technology reduces transaction fees, eliminates the need for third-party verification, and minimizes the expenses associated with manual record-keeping.
5.5 Elimination of Intermediaries
Blockchain technology allows for direct peer-to-peer transactions, bypassing intermediaries such as banks or brokers. This disintermediation reduces delays, enhances privacy, and empowers individuals to have greater control over their assets and data.
6. Challenges and Limitations
6.1 Scalability
The scalability of blockchain technology remains a challenge as the network grows. As more transactions are added to the blockchain, the network’s performance can be affected, leading to slower transaction processing times.
6.2 Regulatory Concerns
The regulatory landscape surrounding blockchain technology is still evolving. Governments and regulatory bodies are grappling with the legal implications of cryptocurrencies, smart contracts, and data privacy, which may impact the widespread adoption of blockchain.
6.3 Energy Consumption
Blockchain networks, particularly those using proof-of-work consensus algorithms, require substantial computational power and energy consumption. Addressing the environmental impact of blockchain mining is crucial for the technology’s sustainable future.
6.4 Integration Issues
Integrating blockchain technology into existing systems can be challenging. Legacy systems and interoperability concerns may hinder the seamless adoption of blockchain across industries, requiring careful planning and collaboration.
6.5 Privacy Concerns
While blockchain provides transparency, privacy concerns arise when sensitive information is stored on a public ledger. Striking a balance between transparency and data protection is crucial for blockchain’s widespread acceptance.
7. Future Trends in Blockchain Technology
The future of blockchain technology looks promising, with several trends shaping its evolution:
- Interoperability: Efforts are underway to enable seamless communication between different blockchain networks, enhancing their compatibility and usability.
- Scalability Solutions: Innovations such as sharding and layer-two protocols aim to address the scalability challenges of blockchain, enabling faster and more efficient transaction processing.
- Enterprise Adoption: More businesses are recognizing the potential of blockchain and incorporating it into their operations, leading to increased adoption across various industries.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Governments are working to establish comprehensive regulatory frameworks that strike a balance between fostering innovation and protecting consumer interests.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: Blockchain is being integrated with emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, Internet of Things (IoT), and edge computing, unlocking new possibilities and use cases.
8. Conclusion
Blockchain technology is transforming the digital landscape by providing secure, transparent, and efficient solutions across industries. Its decentralized nature, coupled with cryptographic security, ensures trust and eliminates the need for intermediaries. While challenges and limitations exist, ongoing advancements and increasing adoption indicate a promising future for blockchain technology.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1. What is blockchain technology? Blockchain technology is a decentralized and transparent system that allows multiple parties to maintain a shared and immutable record of transactions.
Q2. How does blockchain ensure security? Blockchain incorporates advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data and ensure the authenticity and integrity of transactions.
Q3. What are some applications of blockchain technology? Blockchain technology finds applications in finance and banking, supply chain management, healthcare, real estate, voting systems, intellectual property, and more.
Q4. What are the advantages of blockchain technology? Blockchain technology offers enhanced security, transparency, improved efficiency, reduced costs, and the elimination of intermediaries.
Q5. What are the challenges of blockchain technology? Scalability, regulatory concerns, energy consumption, integration issues, and privacy concerns are some challenges associated with blockchain technology.
